Cloud Definition – What is a Cloud? (With Infographic)
The Cloud Is Everywhere
We are used to the cloud. Nevertheless, the concept is rather difficult to grasp. Usually we associate the cloud Dropbox, Google Drive, One Drive & Co. However, the cloud is much more than that. Even if you don’t use any of these online storage services, you will come across the cloud every now and then. Promise.
Do you use Netflix? They store their vast amount of data at Amazon’s AWS. Are you on Pinterest? Guess, where your data is stored. Have you ever travelled and booked a room with Airbnb, or a flight at Expedia? They use the cloud to provide their services, too. Every Google Search you execute is processed with cloud technology. More examples are Adobe, the antivirus software Avira, the film database IMDb, the language teaching app Duolingo, or the review platform yelp. All of those businesses rely on the cloud to provide their services.
In its early days just over 10 years ago, the cloud primarily provided storage and computing capacities online and thus was considered a cheap and convenient alternative for companies to process their more and more increasing amounts of data. Over time, another major advantage emerged: the cloud makes it possible to access resources anywhere and anytime. Today, the cloud represents, beyond the IT infrastructure, also a platform for software development as well as ready-to-use application software in the form of online services.
The cloud is everywhere. Explore the cloud in all its features and benefits for private and business users. Also, learn how to preserve data security and privacy. Get our free infographic "The Cloud - Explained Simply".
Why the Cloud Is Called Cloud
The concept of “cloud” does not prove exactly specific. The initial term “Universal Access Multimedia Data Network" seems more accurate. The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines the cloud as a network of computing resources, such as storage, servers, applications and services, that can be used on-demand anywhere and anytime via the Internet. Nevertheless, the term “cloud” has been established as a vague description of the cloud-like network of resources in datacenters somewhere in the world, which we trust with the processing of our data, without thinking twice.
These data centers are distributed all over the world and are even operated offshore. Each file is stored multiple times in different data centers so that data remains available after a fire or earthquake.
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. (NIST, 2011)
The 5 Essential Characteristics of the Cloud
According to the NIST cloud computing has the following five characteristics:
-
On-Demand Self Service
Users are able to access computing resources by themselves as needed. -
Broad Network Access
The network of resources is available on-demand by using PCs, Laptops and Smartphones anywhere and anytime. -
Resource Pooling
The resources of a provider at different physical locations form a virtual pool, of which users do not exactly have control, let alone knowledge. -
Rapid Elasticity
Resources are provisioned and released rapidly as needed. Contracts on cloud computing are generally short-termed. -
Measured Service
Pay for use. With public cloud storage this means that you choose how much space you need. Plus you can up- and downgrade at any time.
IaaS, PaaS & SaaS - This Sounds More Complicated Than It Is
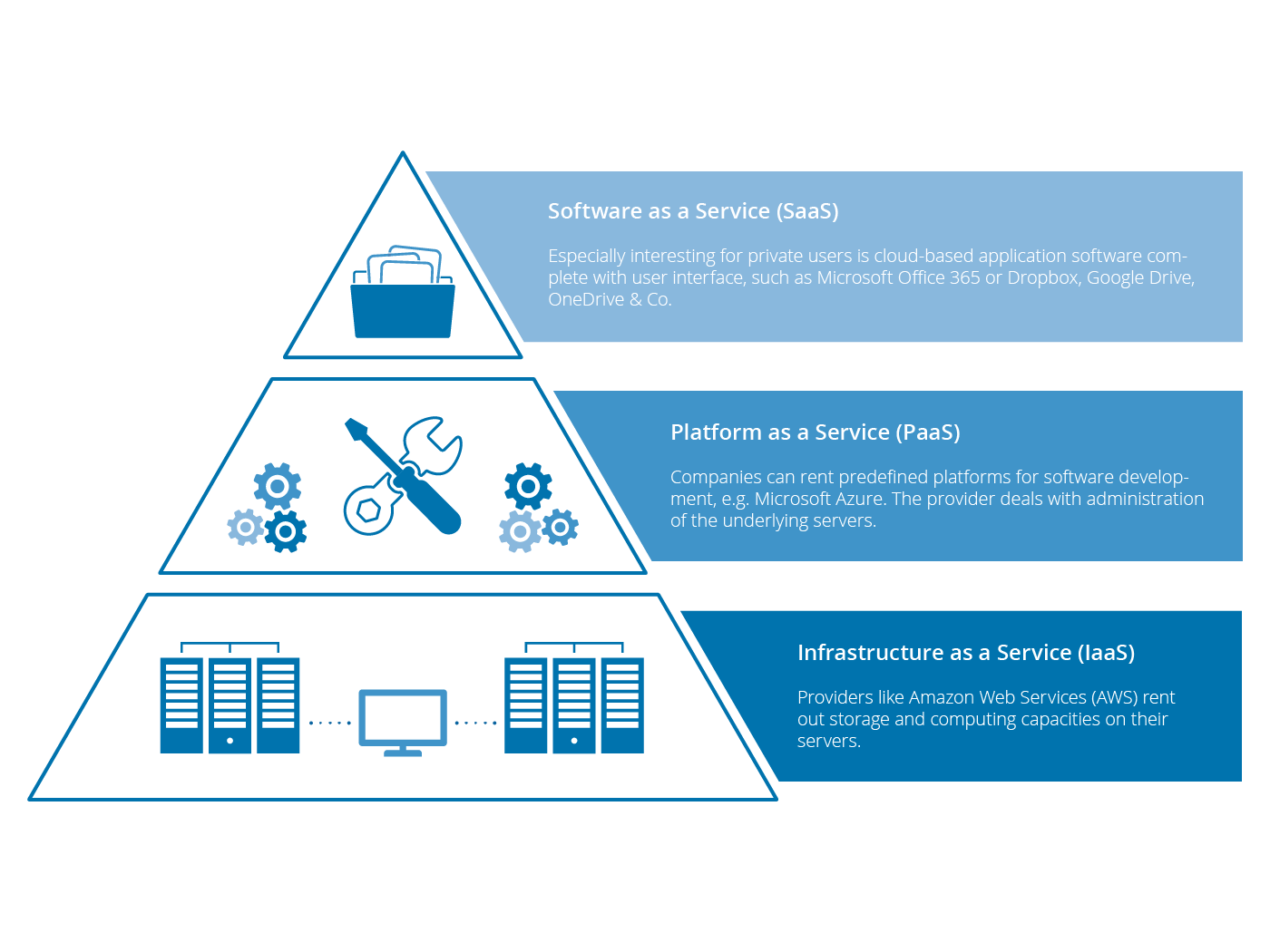
Cloud computing is categorized according to different service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). This is often represented in a pyramid stack model: IaaS is the foundation, PaaS forms the next level up and SaaS the very top.
IaaS
IaaS are basic services providing virtual infrastructure, such as storage and computing capacities. Instead of buying expensive hardware, companies can rent the server capacities they need for their purposes. In total, this saves resources because the capacity rented and used may be easily adapted to the actual need. Although the servers are located in data centers of the provider which the users cannot access, they are still responsible for administration and configuration.
The most popular provider of IaaS is Amazon Web Services: Elastic Cloud Computing (EC2) offers virtual machines, Simple Storage Services (S3) offers storage.
PaaS
PaaS is the next logical step after IaaS. Companies can rent predefined platforms for software development in the cloud. This is often used for the development of applications. The provider of PaaS deals with administration and maintenance of the underlying infrastructure, so that the users can start programming right away.
Popular cloud-based development platforms are AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Microsoft Azure and Google App Engine, supporting common programming languages, such as Python, Java and PHP.
SaaS
SaaS is what most people associate with the cloud. SaaS describes cloud-based application software, which the end-user can access from various devices. Basically the software is rented all-inclusive: the provider takes care of all maintenance of infrastructure and software. Therefore, you do not need to be particularly tech-savvy to use these cloud services. Everything is set up ready-to-use for you. You will interact with a user interface, which you usually cannot modify.
Since 2000, Salesforce with its CRM software has been a pioneer in SaaS solutions for businesses. SAP as well offers cloud-based systems for business processes. Further examples are the Google Apps and Microsoft Office 365, encouraging collaboration and productivity in teams. Especially interesting for private users are probably cloud storage services, like Dropbox, Google Drive and OneDrive.
Benefits of Cloud Solutions
If computers of the kind I have advocated become the computers of the future, then computing may someday be organized as a public utility, just as the telephone system is a public utility. The computer utility could become the basis of a new and important industry. (John McCarthy, 1961)
What the visionary computer specialist predicted as early as 1961 has long come true. His vision was computing that is organized in a similar way as electric power: You pay for what you use, while profiting of a public utility, instead of having to build your own powerhouse in your living room. Now this is exactly what is happing with cloud computing. Instead of every private or business user investing in their own infrastructure, platforms for software development or ready-to-use software, they can simply rent it in the cloud as needed. This saves time, money and quite some trouble. The cloud is a promising technology that will most likely continue to bring change across all industries. In the following, we list some of the benefits of cloud solutions for business and private users.
Benefits of the Cloud for Business Users
- Facilitates virtual collaboration in teams
- Greater flexibility, as the resources of infrastructure, platforms and software are on-demand rented (no need to buy)
- The provider is responsible for IT administration and maintenance
- Especially to small companies hosting offers greater reliability and security of the servers
- Altogether higher productivity at a lower cost
- Cloud computing can turn out to be a decisive competitive advantage
Are you looking for a cloud? Then we might be able to help with a comparison of the best clouds for business use.
Benefits of the Cloud for Private Users
- Convenient synchronization and backup of data on all devices
- You can access your documents, movies, pictures and music anywhere and anytime
- The cloud does not break, get lost or is stolen easily (compared to an external hard drive)
Are you looking for a cloud? Then we might be able to help with a comparison of the best clouds for private use.
What About Security, and Privacy?
Despite all these benefits, people still have doubts about the cloud. They worry about giving up control of their data because they fear an attack on sensitive data or the loss of data. Moreover, there is often uncertainty as to current legislation on data protection.
So this is the good news: Physically your data is secure with all of the large cloud services. The data centers are protected by several security systems, such as armed security personnel, access restriction by electronic IDs, and much more. Therefore, the risk of data being stolen or simply getting lost this way is very low to non-existent. A detailed list of the causes of data loss can be found in our blog article How Data gets Lost.
Data security and privacy are not always guaranteed with cloud offerings. Most providers scan the data synchronized into the cloud for technical reasons. So once your data is encrypted on the server side, providers can easily decrypt it as they have the keys stored. For example, if a government agency requests access to data, the cloud provider can grant it. This has for example been legitimized by the American CLOUD Act.
Another security risk: If hackers manage to gain access to a cloud storage account, they can view data unhindered. We therefore recommend that data in the cloud should always be encrypted on the client side using the "Zero Knowledge" standard. We will explain this topic in more detail in our article Data protection problems in the cloud and explain how you can protect your privacy with "Zero Knowledge" encryption.